A comprehensive survey of wastage and non-revenue water in subscribers of rural water and sewerage company in Mazandaran province
A comprehensive survey of wastage and non-revenue water in subscribers of rural water and sewerage company in Mazandaran province
A comprehensive study of wastage and non-revenue water in the subscribers of rural water and sewerage company in Mazandaran province (pilot)
To the employer of rural water and sewage company of Mazandaran province
Consultant: Babol Nooshirvani University of Technology - Faculty of Mechanics - Dr. Rouzbeh Shafaghat
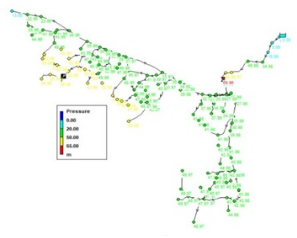
One of the most important issues in water supply networks is the issue of leakage and water losses. Leakage is inevitable in all water distribution systems, even new networks. Among the consequences of water leakage are the need for sources of water supply with appropriate quality, increase in the costs of production, purification, transmission and distribution of water, pollution entering the network, etc. Nowadays, reducing leakage by managing hydraulic parameters such as pressure is of particular importance in addition to leak detection projects. Therefore, in this research, one of the rural network zones of Shirdarkola and Gavankla complex from Babolkanar section of Babol city due to the critical pressure in most of the day and night, the high density of accidents as well as the special topographical conditions and the high height difference of the network compared to the reservoir, from Mazandaran Rural Water and Wastewater Company was selected as a research pilot. This complex has about 1,600 subscribers, 1.88 km of transmission line from the well to the reservoir and 44 km of water supply network with an average production flow rate of 17 and an average sales flow rate of 2.7 liters per second and with a loss of 56.
Research implementation steps and timing:
|
Time table of steps by month |
Title
|
Row
|
|||||||
|
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Field study and recognition of elements |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Checking the amount of production and consumption in the pilot |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specifying problems and the extent of investigation |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investigating and summarizing effective methods in reducing non-revenue water losses |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expressing methods and solutions |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hydraulic modeling of the network |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Design analysis and audit |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Presentation of results and summary |
8 |
Presented articles:
- “Leakage estimation in water networks based on the BABE and MNF analyses: a case study in Gavankola village, Iran” Editor's Choice of Water supply journal
- مقاله "ارزیابی تأثیر مدیریت فشار در کاهش میزان هدررفت واقعی بر مبنای روش آنالیز اجزای نشت زمینه و شکستگی؛ مطالعه موردی" در نهمین کنفرانس بین المللی توسعه پایدار و توسعه شهری
|
executive actions |
Office and research activities |
|
1. Implementation of the collector at the outlet of the tank, installation of flowmeter and its proper distribution between consumption zones 2. Installation of 2 pressure relief valves for areas with excess pressure 3. Replacing the pipe with size 110 polyethylene in the downstream part of Shirdarkla village with a length of approximately 400 meters and installing a valve at the entrance of the main alleys to manage water distribution. 4. Monitoring of the route in zone A (upstream area of Shirdarkola village) and control of the circular network has been established 5. Providing proper pressure in zone A by increasing the head by 10 meters |
1.Establishing isolation areas for investigation (DMA) and investigation of the amount of production and consumption and specifying the problems of each zone. 2. Presenting the algorithm of how to correctly replace the meter of home subscribers 3. Hydraulic analysis of zones with different scenarios with software EPANET.2 4. Correcting the map of the project billet and determining the points of valves and important connections of the network 5. Providing a fracture density map and determining the priority of pipe replacement and corrective measures 6. Presenting the daily and monthly consumption patterns of the rural sector |
Comparison of the system before and after the implementation of the operation
|
After running the operation |
Before executing the operation |
|
Average pressure: 41 meters Number of fractures: 3 events per month Water loss rate: 1.4 liters per second |
Average pressure is 86 meters Number of fractures: 38 cases per month Water loss rate: 4 liters per second |
890 million Rials annual cost reduction
 |
 |
 |